Related Content
The Myotonic Dystrophy Foundation US made the following grants in 2023:
2023 MDF Early Career Researchers
Dylan Farnsworth, PhD
Senior Research Scientist
The RNA Institute, University of Albany, New York, US
The Myotonic Dystrophy Foundation US made the following Research Fellowship grants in 2023:
Mackenzie Davenport, PhD
University of Florida, Gainesville, Florida, US
In partnership, the Myotonic Dystrophy Foundation US and the Myotonic Dystrophy Foundation UK made the following Research Fellowship grants in 2022.
In partnership, the Myotonic Dystrophy Foundation US and the Myotonic Dystrophy Foundation UK made the following Research Fellowship grants in 2021.
In partnership, the Myotonic Dystrophy Foundation US and the Myotonic Dystrophy Foundation UK made the following grants in 2015.
In partnership, the Myotonic Dystrophy Foundation US and the Myotonic Dystrophy Foundation UK made the following grants in 2016.
In partnership, the Myotonic Dystrophy Foundation US and the Myotonic Dystrophy Foundation UK made the following grants in 2017.
In partnership, the Myotonic Dystrophy Foundation US and the Myotonic Dystrophy Foundation UK made the following grants in 2018.
In partnership, the Myotonic Dystrophy Foundation US and the Myotonic Dystrophy Foundation UK made the following grants in 2019.
In partnership, the Myotonic Dystrophy Foundation US and the Myotonic Dystrophy Foundation UK made the following grants in 2020.
The following Research Fellowship grants were awarded in 2009.
The following Research Fellowship grants were awarded in 2010.
The following Research Fellowship grants were awarded in 2011.
The following Research Fellowship grants were awarded in 2012.
The following Research Fellowship grants were awarded in 2013.
The following Research Fellowship grants were awarded in 2014.
In partnership with the Myotonic Dystrophy Foundation US, the Myotonic Dystrophy Foundation UK made the following Research Fellowship grants in 2015.
In partnership with the Myotonic Dystrophy Foundation US, the Myotonic Dystrophy Foundation UK made the following Research Fellowship grants in 2016.
In partnership with the Myotonic Dystrophy Foundation US, the Myotonic Dystrophy Foundation UK made the following Research Fellowship grants in 2017.
In partnership with the Myotonic Dystrophy Foundation US, the Myotonic Dystrophy Foundation UK made the following Research Fellowship grants in 2018.
In partnership with the Myotonic Dystrophy Foundation US, the Myotonic Dystrophy Foundation UK made the following Research Fellowship grants in 2019.
In partnership, the Myotonic Dystrophy Foundation US and the Myotonic Dystrophy Foundation UK made the following Research Fellowship grants in 2020.
If your health plan denies you coverage or refuses to pay a claim, you have the right to appeal that decision or have it reviewed by a third party. If your appeal is accepted, you can be reimbursed by your insurance company for the services that they failed to cover.
The first-line of decision making about a health plan’s coverage is typically made by a utilization review manager/case manager. If your provider prescribes you a service for DM, this utilization review manager will conduct a utilization review before your insurance company can approve coverage.
People with DM are often denied coverage for medications and services that are not listed in their insurance formularies. Because DM is a rare disease, insurance companies are often not aware of the symptom management strategies that are medically necessary for people living with DM.
There are two main categories of health insurance - private and public.
Some of the most common questions received by Myotonic involve issues with health insurance coverage for people living with myotonic dystrophy (DM).
It is important to understand how CTG repeat length is associated with the severity of myotonic dystrophy type 1. CTG is the type of trinucleotide repeat expansion found on the DPMK gene inherited by individuals with DM1.
Learn more about the patterns, symptoms, diagnosis and treatments available for Skin problems in CDM.
Learn more about the patterns, symptoms, diagnosis and treatments available for Skin problems in DM2.
Learn more about the patterns, symptoms, diagnosis and treatments available for Skin problems in DM1.
Learn more about the patterns, symptoms, diagnosis and treatments available for Gastrointestinal System problems in CDM.
Learn more about the patterns, symptoms, diagnosis and treatments available for Gastrointestinal System problems in DM2.
Learn more about the patterns, symptoms, diagnosis and treatments available for Gastrointestinal System problems in DM1.
Learn more about the patterns, symptoms, diagnosis and treatments available for Cardiovascular System problems in CDM.
Learn more about the patterns, symptoms, diagnosis and treatments available for Cardiovascular System problems in DM2.
Learn more about the patterns, symptoms, diagnosis and treatments available for Cardiovascular System problems in DM1.
Learn more about the patterns, symptoms, diagnosis and treatments available for Genetic problems in CDM.
Learn more about the patterns, symptoms, diagnosis and treatments available for Genetic problems in DM2.
Learn more about the patterns, symptoms, diagnosis and treatments available for Genetic problems in DM1.
Learn more about the patterns, symptoms, diagnosis and treatments available for Vision problems in CDM.
Learn more about the patterns, symptoms, diagnosis and treatments available for Vision problems in DM2.
Learn more about the patterns, symptoms, diagnosis and treatments available for Vision problems in DM1.
Learn more about the patterns, symptoms, diagnosis and treatments available for Muscle problems in CDM.
Learn more about the patterns, symptoms, diagnosis and treatments available for Muscle problems in DM2.
Learn more about the patterns, symptoms, diagnosis and treatments available for Muscle problems in DM1.
Learn more about the patterns, symptoms, diagnosis and treatments available for Reproductive System problems in CDM.
Learn more about the patterns, symptoms, diagnosis and treatments available for Reproductive System problems in DM2.
Learn more about the patterns, symptoms, diagnosis and treatments available for Reproductive System problems in DM1.
Learn more about the patterns, symptoms, diagnosis and treatments available for Endocrine System problems in CDM.
Learn more about the patterns, symptoms, diagnosis and treatments available for Endocrine System problems in DM2.
Learn more about the patterns, symptoms, diagnosis and treatments available for Endocrine System problems in DM1.
Learn more about the patterns, symptoms, diagnosis and treatments available for Respiratory System problems in CDM.
Learn more about the patterns, symptoms, diagnosis and treatments available for Respiratory System problems in DM2.
Learn more about the patterns, symptoms, diagnosis and treatments available for Respiratory System problems in DM1.
Learn more about the patterns, symptoms, diagnosis and treatments available for Central Nervous System problems in CDM.
Learn more about the patterns, symptoms, diagnosis and treatments available for Central Nervous System problems in DM2.
Learn more about the patterns, symptoms, diagnosis and treatments available for Central Nervous System problems in DM1.
Links to presentations for sessions and meetings included in the 2016 Myotonic Annual Conference Professionals Track are provided below, when available.
The 2016 Myotonic Annual Conference Community Track included the following sessions below. You'll find links for the presentations and videos from those sessions linked below if they are available.
www.bridgingapps.org - a program and website of Easter Seals Greater Houston that provides resources, education, and information on apps and mobile devices to help people with disabilities target and improve skills and reach their highest
To find out more information about art therapy, or to find a referral to an art therapist near you, check out www.arttherapy.org locate your local art therapy chapter and request an art therapy referral.
The following organizations help promote, certify and regulate Acupuncture and Asian Medicine in the United States. A prospective patient can visit the websites to further research acupuncture as well as find a practitioner in their area.
If you are a newcomer to the Myotonic community, you may be a little overwhelmed by the wealth of materials and information that you're presented with at the 2015 Myotonic Annual Conference.
July 2016
-
Myotonic Dystrophy Meeting: Developing a European consortium for care and therapy. European Neuro Muscular Centre. July 1-3, Naarden, Netherlands.
April 2016
- 68th American Academy of Neurologists Meeting. Apr. 15-21, Vancouver, B.C. Abstract submission will open in early September 2015.
- Global Orphan Drug Conference and Expo. Apr. 20-22, Washington, D.C.
May 2016
U.S. Department of Education: A Guide to the Individualized Education Program: http://www2.ed.gov/parents/needs/speced/iepguide/index.html#introduction
Washington State Father’s Network:
Join the Myotonic Caregivers Facebook Group: https://www.facebook.com/groups/271639446333878/
This trial has produced a lot of interest and excitement. It is important to realize, however, that just because an investigational compound is “tailor made” doesn’t mean that it will be safe or even effective; the purpose of a clinical trial is to find that out.
The Food and Drug Administration has issued a call for information about biomarkers in development.
Thursday, September 17: Pre-Conference Activities
3:00 - 7:00 PM
Myotonic has been working with partners in other rare disease organizations, Congress, and biotech/pharma in order to improve the regulatory review and drug approval processes in the US.
Isis Pharmaceuticals Initiates Phase 1/2 Study of ISIS-DMPK Rx in Patients with Myotonic Dystrophy Type 1
MDF Recognizes Rare Disease Month by Unveiling Hope and Inspiration Video
Isis has completed a Phase 1 study evaluating the safety of ISIS-DMPKRx in healthy volunteers. In this study, ISIS-DMPKRx was well tolerated at all dose levels tested with no safety or tolerability concerns. The compound was delivered by a subcutaneous injection.
Multi-Disease Organizations
-
National Organization of Rare Disorders (NORD)
NORD is an organization that provides information on rare disease issues, legislation, and related topics.
You may view past webinars at any time on the Myotonic Digital Academy.
You need access to a high-speed Internet-connected computer with either the ability to play audio or use of a separate telephone line. Webinars include a slide presentation and/or live streaming video and audio.
System requirements for attending a session include:
Here's what you'll need to do to attend our webinars live:
Myotonic dystrophy is associated with a modest reduction in the amount of immunoglobulin in the blood (hypogammaglobulinemia). The production of antibodies is normal, however the antibodies do not last as long in the circulation, hence the amount in the blood at any time is somewhat reduced.
People with myotonic dystrophy DM1 have an increased frequency of pilomatrixoma, a type of benign skin tumor. This type of tumor is rare in the general population but fairly common in people with myotonic dystrophy DM1. (No association between pilomatrixomas and DM2 has been reported).
Annual Ophthalmological Examination
Annual eye examinations should be done on every DM1 and DM2 patient to assess above-described eye problems.
Myotonic reserves the right to delete, modify, or supplement the content herein at any time for any reason without liability or notification to anyone.
Any closed Facebook groups, forums or membership sections associated with the Myotonic website or the Myotonic Blog are for the use of people affected by DM and their families, and are maintained as semi-restricted forums.
Information published on this site and opinions offered by individuals on this blog and other linked sites are provided for educational and informational purposes only.
When used in this agreement, the term "Copyright" shall be understood to mean any and all rights that protect original works of authorship fixed in any tangible medium of expression, now known or later developed, from which they can be perceived, reproduced, or otherwise communicated, either dire
Myotonic is a charitable organization pursuant to a tax exemption granted under §501(c)(3) of the United States Internal Revenue Code.
Introduction:
- Download: download the SpeakingPhoto app (it’s free!) to your tablet or smartphone.
- Open and Shoot: open SpeakingPhoto and select SHOOT to take a new picture (or SPEAK to use one from your camera roll).
Download this letter and edit the red text before copying and pasting the text into an email.
First introduced as part of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, the Orphan Drug Tax Credit has allowed drug manufacturers to claim a tax credit of 50% of certain research costs for orphan drugs (drugs for diseases affecting 200,000 Americans or fewer).
For more information on the 21st Century Cures Act, please visit the advocacy page on the Myotonic website.
The following is a brief description of the two chambers of Congress and what their functions are:
The barrage of government and procedural jargon is often confusing and off-putting for new advocates. This glossary is designed to help you learn some of the more commonly-used terms in the lawmaking process.
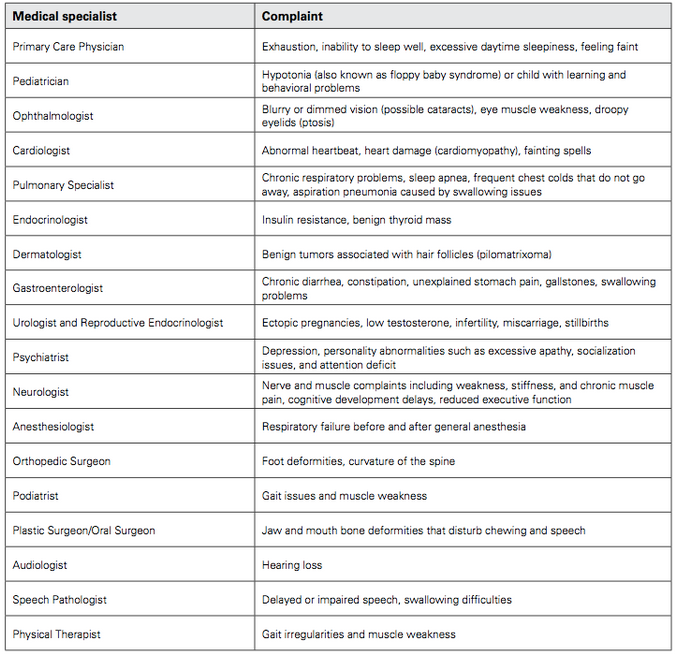
 The Find a Doctor tool is a collection of practitioners that DM patients have seen for their condition.
The Find a Doctor tool is a collection of practitioners that DM patients have seen for their condition.
Grassroots advocacy is citizen participation in government. The key to successful advocacy is assembling people who share common goals and concerns. Advocacy is all about educating legislators about the opinions and views of their voting constituents.
As part of our 2014 commitment to grow and deepen our advocacy program and incorporate grassroots advocacy in our efforts, MDF will feature our first-ever advocacy track at the MDF Annual Conference, which will be held this year in Washington, DC, on September 12-13, 2014.
Learn how to find the local district offices for your members of Congress, as well as how to begin a dialogue with them that will help educate them about myotonic dystrophy! Watch a video of the training here.
A variety of organizations exist in the United States and around the world to support people living with myotonic dystrophy. For more information and links to organizations in your area, click here.
Myotonic Dystrophy – Present Management, Future Therapy, edited by Prof. Peter Harper, published by Oxford University Press, 2004. A 240-page book written by DM experts from around the world, geared to medical professionals.
Click here to visit Myotonic Dystrophy Family Registry website, learn more and sign up.
Your participation is voluntary and your individual information will be kept completely confidential. You can opt out of the Registry at any time and all of the data you provide will be entirely de-identified (anonymous).
Because you will have access to de-identified information in the Registry, you can learn more about DM, how it's experienced by other community members, and what the broader community looks like. This includes:
By joining the Myotonic Dystrophy Family Registry, you will aid researchers, pharmaceutical companies and other professionals seeking to:
...Are there any additional risks for an affected woman during pregnancy? Are there any precautions she should take if she becomes pregnant?
What is the relationship between sleep apnea and DM? Modafinil is the choice although it is expensive. Sleep apnea contributes to the daytime somnolence but patients often continue to have daytime sleepiness after CPAP.
...And is there information on rate of successful pregnancy when the woman does not have DM?
...Recognizing that exercise does not prevent the progression of muscle weakness in DM, are there exercise regimens that are recommended to try and maintain what muscle strength is present?
...What emergency interventions should be followed? Does chewing food a lot help food go down easily? Does drinking lots of liquids with a meal help? Any particular type of liquid?
...Are these related to the following: a) digestion, b) type of food eaten, c) muscles not working properly? How can these problems be treated?
...How should a DM patient be followed from a cardiac standpoint (e.g. EKGs, echos, etc.)?
Note: An example of a serious cardiac problem would include a very rapid or very slow heartbeat, or arrhythmia (irregular heartbeat).
Perioperative complication is increased in patients with DM. All drugs, including sedatives, induction drugs, anesthetics, neuromuscular junction blockers and opiates must be carefully chosen, and doses must be carefully determined. In particular, anticholiesterases (e.g.
For information on how DM affects executive function, see the Body Systems Tool.
...Is it larger with maternal transmissions? Or is there an identical distribution between men and women?
Not always. Their genetic background is different although many genes are shared. The genomic background is likely to play an important role in organ-specific phenotype expression.
No treatments currently exist that slow the progression of myotonic dystrophy, but symptomatic treatments are available. Managing the symptoms of this disease can reduce suffering and improve quality of life for patients.
Myotonic dystrophy is a progressive or degenerative disease. Symptoms tend to worsen gradually over several decades. While no treatment exists that slows the progression of myotonic dystrophy, management of its symptoms can greatly improve patient quality of life.
A complete diagnostic evaluation, which includes family history, physical examination, and medical tests, is typically required for a presumptive diagnosis of myotonic dystrophy.
Myotonic dystrophy is an inherited disease where a change, called a mutation, has occurred in a gene required for normal muscle function. The mutation prevents the gene from carrying out its function properly.
There are two well-defined types of the disease (DM1 and DM2) which have distinct but overlapping symptoms.
Muscular dystrophy (MD) refers to a group of nine genetic diseases that cause progressive weakness and degeneration of muscles used during voluntary movement. Myotonic dystrophy (DM) is one of the muscular dystrophies.
- Myotonic muscular dystrophy - often abbreviated as MMD
- Dystrophia myotonica - a Latin name used by many doctors; often abbreviated as DM. The different types of DM are typically referred to as DM1 or DM2.
Myotonic dystrophy (DM) is a multi-systemic inherited disease that affects at least 1 in 2,100 people or over 150,000 individuals in the US alone (Johnson 2021).
ZNF9. The mutated gene on chromosome 3 that causes DM2; sometimes called the zinc finger gene.
Tachyarrhythmia. Very rapid heart beats.
Talipes equinovarus. An inversion of the foot in which only the outer side of the sole touches the ground; also called club foot.
Section 504. Individuals with disabilities may not be excluded from participating in programs and services receiving federal funds. It also prohibits job discrimination against people with disabilities in any program receiving federal financial assistance.
Respiratory function test. A test that measures the amount of air a person can blow out.
PCR - polymerase chain reaction. A procedure that produces millions of copies of a short segment of DNA; the amplified product, doubled each cycle for 30 more cycles, can then be subjected to further testing; it is a common procedure in molecular genetic testing in order to gener
Newborn screening. Public health program of screening in infants shortly after birth for conditions that are not clinically evident in the newborn period.
NICU. Neonatal (new born) intensive care unit.
Mexiletine. A drug used to treat myotonia (delayed muscle relaxation after contraction) in muscle diseases such as myotonic dystrophy and myotonia congenital (brand name is Mexitil).
Implanted Cardioconverter Defibrillator (ICD). A cardiac device implanted in the chest; a combination pace-maker and defibrillator designed to regulate the heart beat, to keep it from beating too fast or too slow.
Haplotype analylsis. Molecular genetic testing to identify a set of closely linked segments of DNA.
Gait. Manner of walking.
Gastroenterologist. A doctor focusing on the function and disorders of the stomach, intestines and assorted organs that are often referred to as the GI tract.
Foot drop. Partial or total inability to dorsiflex (turn upward) the foot.
Formulary. A list of prescription drugs covered by a prescription drug plan or another insurance plan offering prescription drug benefits. Also called a drug list.
Ectopic. Occuring in the wrong place in the body, such as the development of an impregnated egg outside the cavity of the uterus; or, a cardiac beat originating elsewhere other than at the sinoatrial node.
EDS. Acronym for excessive daytime sleepiness.
Deductible. The amount you pay for covered healthcare services before your insurance plan starts to pay. With a $2,000 deductible for example, you pay the first $2,000 of covered services yourself.
Cataracts. A film that can form in the eye and cause complete or partial opacity of the ocular lens, or blurry vision; in myotonic dystrophy patients, often posterior subcapsular iridescent cataracts form; they are sometimes referred to as Christmas-tree cataracts.
Barium swallow test. A test in which a patient swallows a thick white substance and the swallowing process is filmed to detect possible abnormalities.
Blepheroplasty. Any operation for the correction of a defect in the eyelids.
Accommodations. Supports that are provided to a child throughout the school day that do not significantly alter what is being taught or how the child participates in school activities.
In patients with myotonic dystrophy, there is a problem with a particular gene that causes it to convey faulty instructions. This mistake results in the symptoms of DM. The two forms of myotonic dystrophy are caused by mutations in different genes.
DNA is the genetic material found in the nucleus of nearly every cell. A gene is a stretch of DNA that carries a set of instructions on how a protein should be made. These proteins carry out the functions of the body. Scientists estimate that humans have about 25,000 different genes.
Both DM1 and DM2 are passed from parent to child by autosomal dominant mutations. This means that the faulty gene is located on one of the chromosomes that does not determine sex (autosome) and that one copy of the mutated gene is enough to cause the disease (dominant).
Studies have been done to understand how these non-coding mutations could have a trans-dominant effect (i.e. how they could affect other genes not associated with the mutation locus). This research suggests a gain-of-function RNA mechanism underlies the clinical features common to both diseases.
Myotonic dystrophy is one of the most complex disorders known. In addition to the incredible variability of clinical symptoms, the disease also has unique mechanistic features:
Myotonic dystrophy is one of the most complex disorders known. In addition to the incredible variability of clinical symptoms, the disease also has several unique mechanistic features:
Additional forms (DM3 and DM4) have been suggested, as a small number of individuals have been seen who have the characteristics symptoms of myotonic dystrophy, but who do not have the genetic mutations which cause these disorders.
Myotonic dystrophy type 2, also known as proximal myotonic myopathy (PROMM), is a milder form of myotonic dystrophy in which transient muscle pain is the most common complaint. Only adult-onset forms of DM2 have been recognized.
DM1 (also known as Steinert's disease) is the most prevalent form of the condition and generally the most severe.
Myotonic dystrophy is a progressive or degenerative disease. Symptoms tend to worsen gradually over several decades. While no treatment exists that slows the progression of myotonic dystrophy, management of its symptoms can greatly improve patient quality of life.
- If you haven't already done so, register to vote to make your voice heard on important issues!
Find out the proper way to write, email, or call your members of Congress.
Enter your ZIP code to determine which Congressional District you live in, and to find contact information for your members of Congress.
Read about the issues that are the most important to the DM community! In 2015, we are advocating for improvement in the regulatory review process, largely focusing on the 21st Century Cures Initiative.
Myotonic regularly presents advocacy webinars explaining our current issues and campaigns, and provides advocacy trainings at our annual conference.
A great way to familiarize your members of Congress with DM and your family's story is to give them a packet of information. To find your member of Congress' district office locations, please refer to the House of Representatives
It will only take a minute, but it can mean so much to those living with DM!
December 2012 Dispatch
- Coming Soon: the MDF Patient Registry
- Double the Impact of Your Gift to MDF This Season
December 2014 Dispatch
- Webinar: Clinical Trials 101
- Sarah and Zoé Berman: A Story of Hope and Recovery